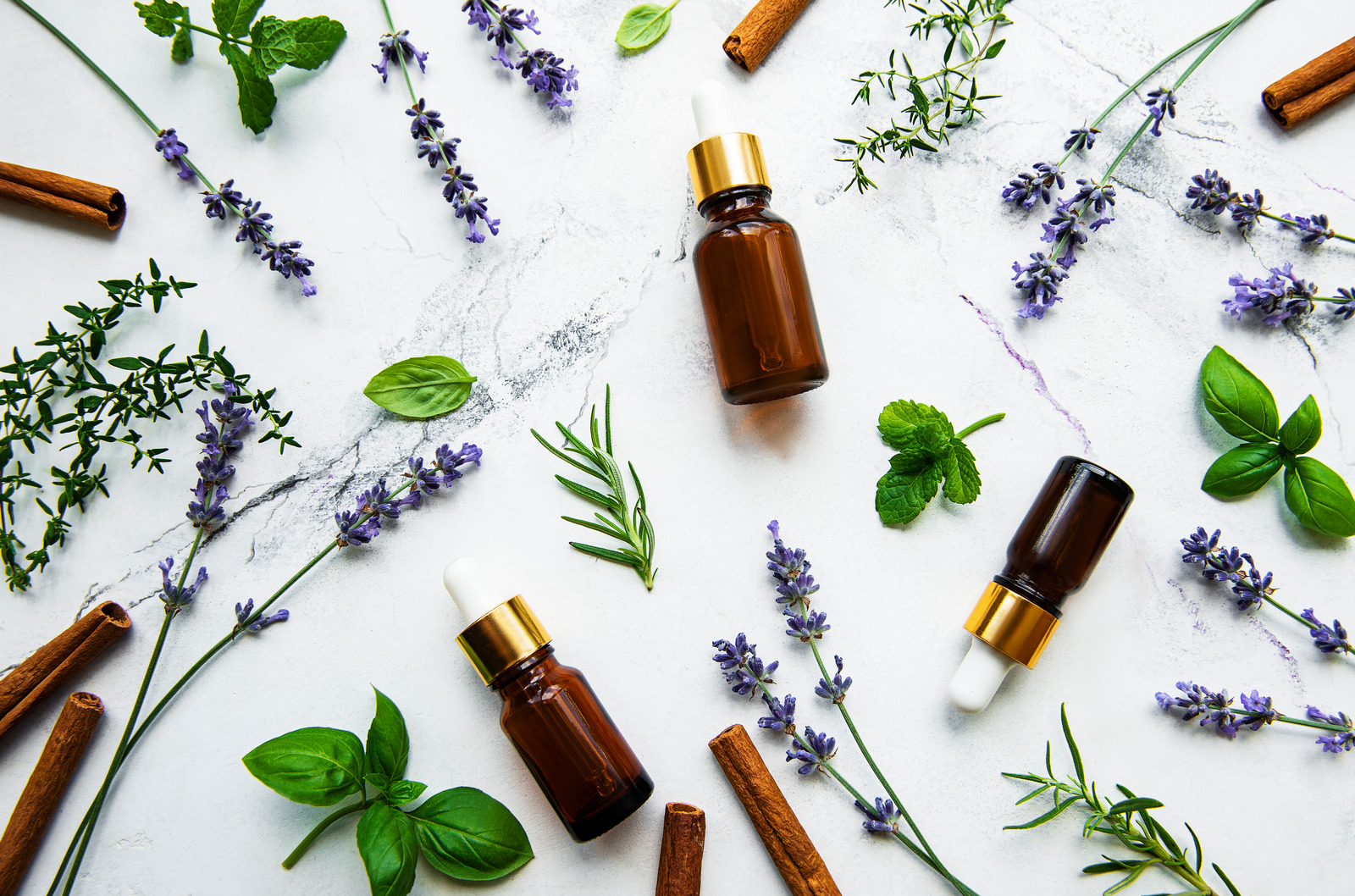
Plants used for protection against diseases, treatment and health are called Medicinal Plants, and plants that give odour and flavour are called Aromatic Plants. Plants that can be used in both sectors are called Medicinal and Aromatic plants.
Medicinal and aromatic plants are used in different industrial branches such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, perfumes, creams, soaps, teas, spices, flavours, etc. in different forms such as raw plant or herbal extract, essential oil and fixed oil.
As examples of medicinal aromatic plants in our country; Aronia, Rosemary, St. John's Wort, Poppy, Lavender, May Chamomile, Myrtle, Baby's Breath, Red Pepper, Pot Marigold Flower, Passionflower, Mustard, Thyme, Aniseed, Ginger, Garlic, Curcumin, etc. can be listed as follows.
Flavour is an important quality standard for unrefined herbal oils, especially those whose trial and acceptability are highly dependent on flavour characteristics. All other techniques, including extraction, separation, detection and identification in flavour-oriented studies, allow the identification of hundreds of volatile compounds and aroma-active compounds of high complexity. With the progress and development of analytical techniques, it provides a better and deeper understanding of volatile compounds in herbal oils quantitatively.
From ancient times to the present day, people have preferred herbal products in the prevention and treatment of diseases. In recent years, in the face of increasing knowledge and demand for green and sustainable ingredients, it is possible to find natural raw materials, herbal oils in most medical drugs. Antioxidants contained in herbal oils prevent cancer and other diseases and strengthen immunity.
Herbal oils are also a very important raw materials for the cosmetics industry due to the antioxidants and vitamins they contain. Hundreds of different plants are used in cosmetic products, especially skin products.